| (2025.10) New Insights In-Plane Porous Defects Formation Mechanism of Single-Layer Graphitic Carbon Nitride by Tetrahydrofuran Etching Reaction | |||||
| 작성자 | 관리자 | 작성일 | 2025-11-19 | 조회수 | 53 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
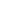
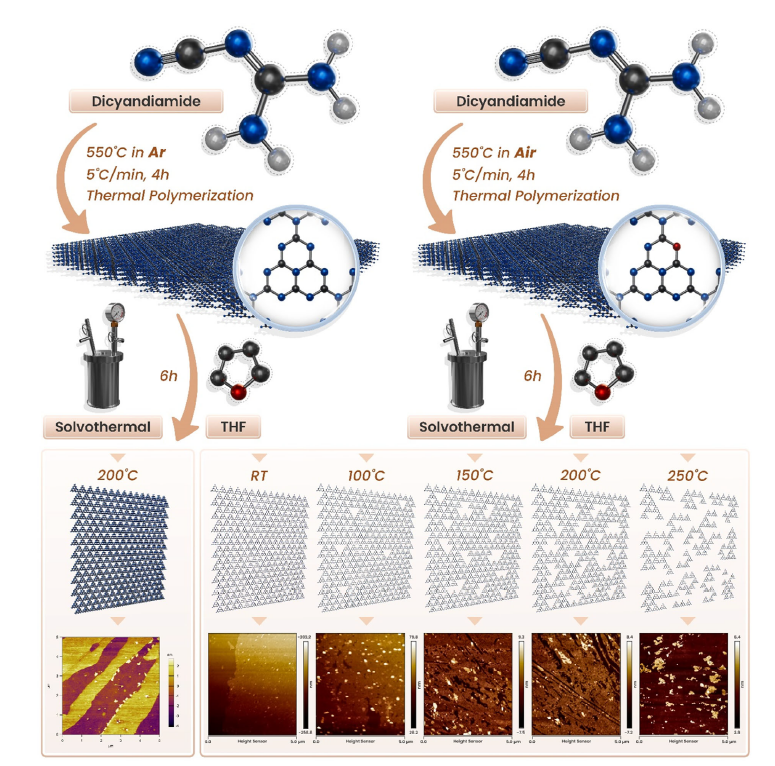
· 논문명 : New Insights In-Plane Porous Defects Formation Mechanism of Single-Layer Graphitic Carbon Nitride by Tetrahydrofuran Etching Reaction · 저 자 : Nam Le, Thanh Truong Dang, Tam Van Tran, Won Mook Choi*, Jin Suk Chung*, Seung Hyun Hur* · 게재지 : Small Structures (2025, 6, 2500259) · 초록 Defect engineering is an effective way to accelerate catalytic yield of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4). Herein,bulk g-C3N4 is synthesized under two calcination atmospheres, argon and air, which significantly influence the incorporation of oxygen into the g-C3N4 structure and the formation of nitrogen vacancy. The oxygen doping and nitrogen vacancy play an essential role in promoting the creation of in-plane porous defects by etching reaction with tetrahydrofuran(THF), while the in-plane porous defect contents are controlled by optimization of the reaction temperature. The best CN-200-Pt sample achieves an excellent photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of 7806.6 μmol g-1 h-1, and an optimal photocurrent density reached 1.8 μA cm-2, representing 11 times and 9 times enhancements over the nondefective BCN–Ar–Pt sample, respectively. These results demonstrate that the controlled introduction of in-plane porous defects can effectively modulate the charge separation process, number of catalytic active sites, band structure, and Pt2+/Pt0 cocatalyst sites, directly enhancing the photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical water-splitting performance of g-C3N4. Along with density functional theory and molecular dynamics calculations, this study suggests the role of oxygen doping and nitrogen vacancy for the formation of in-plane porous defects in the 2D g-C3N4 nanosheets in the etching reaction by THF, thus highlighting its potential in practical applications.
|
|||||