| (2023.09) Versatile, Stable, and Scalable Gel-Like Aerophobic Surface System (GLASS) for Hydrogen Production | |||||
| 작성자 | 관리자 | 작성일 | 2024-06-10 | 조회수 | 37 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
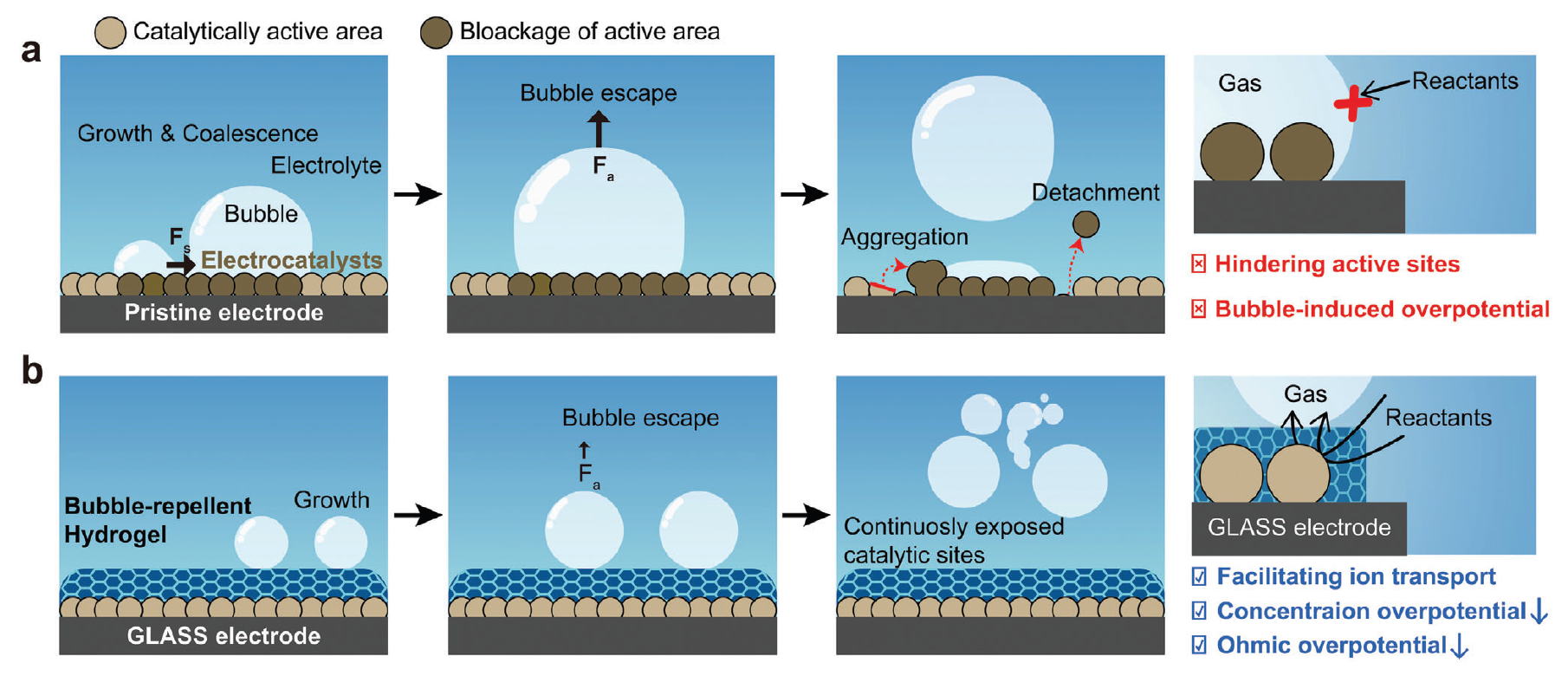
· 논문명 : Versatile, Stable, and Scalable Gel-Like Aerophobic Surface System (GLASS) for Hydrogen Production · 저 자 : Yunseok Kang, Seunghyun Lee, Seongsoo Han, Dasom Jeon, Misol Bae, Yuri Choi, Dong Woog Lee, Jungki Ryu* · 게재지 : Advanced Functional Materials (2024. 34, 2308827) · 초록 Facile removal of adsorbed gas bubbles from electrode surfaces is crucial to realize efficient and stable energy conversion devices based on electrochemical gas evolution reactions. Conventional studies on bubble removal have limited applicability and scalability due to their reliance on complex and energy/time-intensive processes. In this study, a simple and versatile method is reported to fabricate large-area superaerophobic electrodes (up to 100 cm2) for diverse gas evolution reactions using the gel-like aerophobic surface system (GLASS). GLASS electrodes are readily and uniformly fabricated by simple spin-coating and cross-linking of polyallylamineon virtually any kinds of electrodes within 5 min under ambient conditions.Intrinsically hydrophilic gel overlayers with interconnected open pores allow the physical separation of bubble adhesion and catalytic active sites, reducing bubble adhesion strength, and promoting the removal of gas bubbles. As a result, GLASS electrodes exhibit greatly enhanced efficiency and stability for diverse gas evolution reactions, such as hydrogen evolution, hydrazineoxidation, and oxygen evolution reactions. This study provides deepe rinsights into understanding the effect of the hydrophilic microenvironment on gas evolution reactions and designing practical electrochemical devices.
|
|||||