| (2024.05) Tailoring hydrophilic and hydrophobic microenvironments for gas–liquid–solid triphase electrochemical reactions | |||||
| 작성자 | 관리자 | 작성일 | 2024-06-11 | 조회수 | 105 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
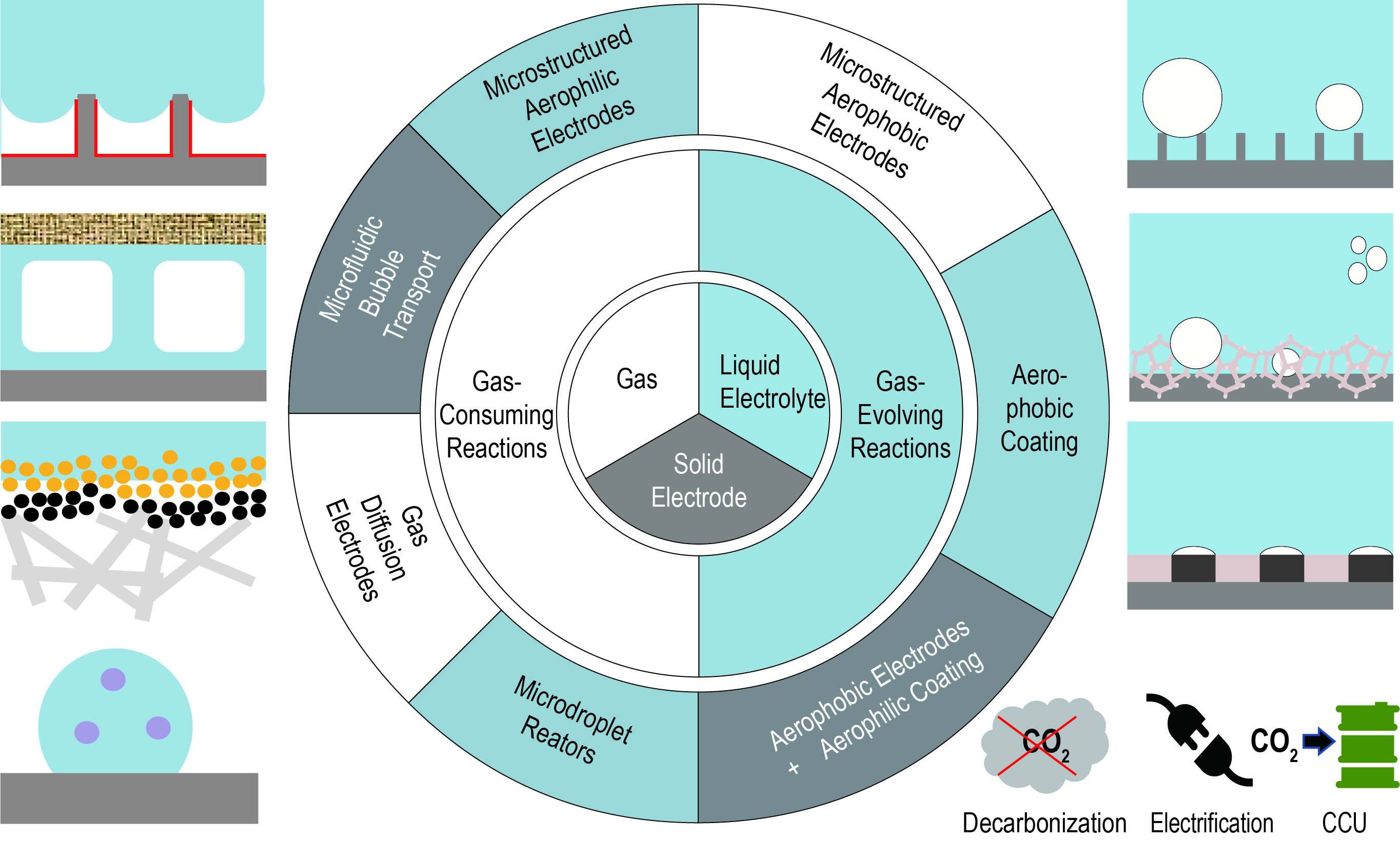
· 논문명 : Tailoring hydrophilic and hydrophobic microenvironments for gas–liquid–solid triphase electrochemical reactions · 저 자 : Jungki Ryu*, Dong Woog Lee* · 게재지 : Journal of Materials Chemistry A (2024, 12, 10012-10043) · 초록 Electrochemical reactions involving gaseous chemicals as reactants or products have the potential to play a critical role in transitioning to a sustainable, carbon-neutral society. Such reactions include gas-evolving reactions (e.g., the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), oxygen evolution reaction, and chlorine evolution reaction) and gas-consuming reactions (e.g., the carbon dioxide reduction reaction, nitrogen reduction reaction, and oxygen reduction reaction). For efficient and stable production of desired chemicals via these reactions, it is imperative to develop rational strategies for managing gaseous chemicals, as well as properly design electrocatalysts. For gas-evolving reactions, efficient gas bubble removal from electrodes is crucial, as gas bubbles can adhere to the electrodes, lowering efficiency and stability due to inefficient mass transport and repeated stress cycles. Conversely, gas-consuming reactions require an effective supply of gaseous reactants and suppression of competing HER for efficient, selective target chemical production. In this review, we summarize recent studies on controlling the hydrophilic and hydrophobic microenvironment of electrodes to address these issues and suggest characterization practices and future perspectives for practical applications. We believe this article provides valuable insights and will inspire researchers in various fields to design innovative electrochemical systems for carbon neutrality.
|
|||||